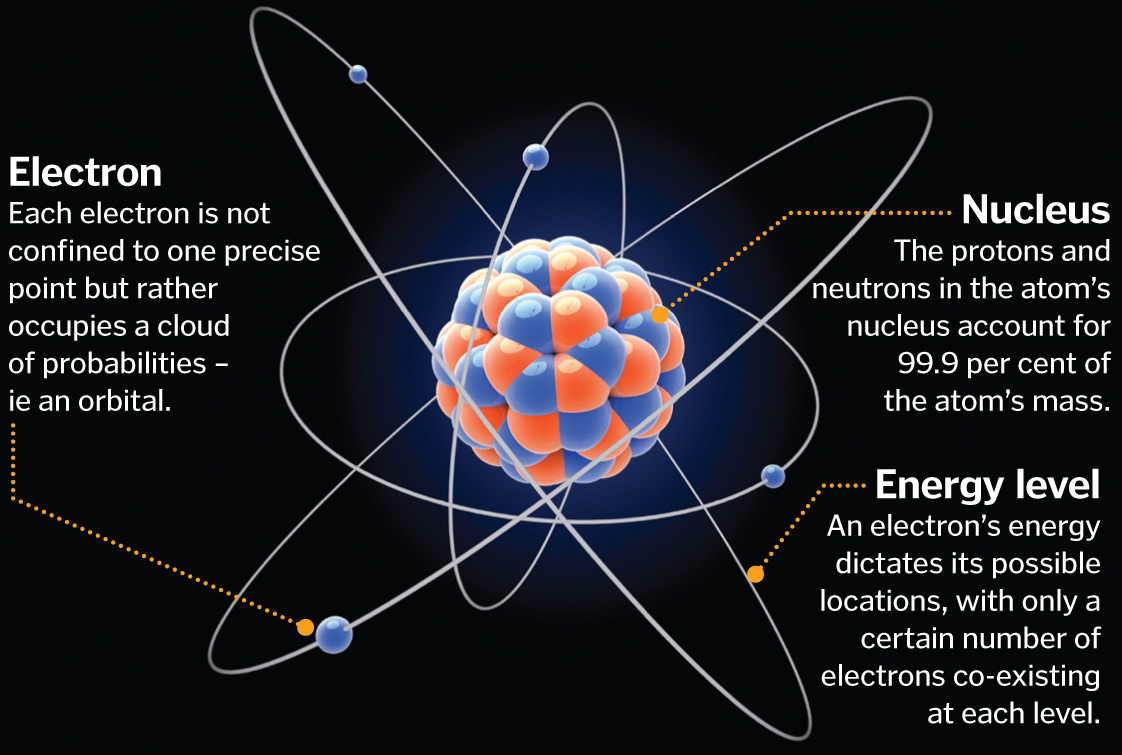
The atoms that make up the world around us seem solid, but are in fact
over 99.99999 per cent empty space. An atom consists of a tiny, dense
nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons, spread over a
proportionately vast area. This is because as well as being particles,
electrons act like waves. Electrons can only exist where the crests and
troughs of these waves add up correctly. And instead of existing in one
point, each electron’s location is spread over a range of probabilities –
an orbital. They thus occupy a huge amount of space.
A nucleon (proton or neutron) is about 1.5 femtometers across, which is 1.5x10-15 meters. So the number density of nuclear matter is about 0.1 nucleons per cubic fermi, or 0.1 fm-3. I don't have a source for these and I don't care to google it; these are just the numbers I have at my finger tips for my research, but if you'd like to know more you can google the "nuclear saturation density."
Anyway, if the average person has a mass of about 60 kg, and that mass is 99.99% in the nucleons, then we can just take the number of humans in the world times their mass, divide by the nuclear mass density (which is the number density times the mass of a nucleon).
A nucleon (proton or neutron) is about 1.5 femtometers across, which is 1.5x10-15 meters. So the number density of nuclear matter is about 0.1 nucleons per cubic Fermi, or 0.1 fm-3. I don't have a source for these and I don't care to google it; these are just the numbers I have at my finger tips for my research, but if you'd like to know more you can google the "nuclear saturation density."
Anyway, if the average person has a mass of about 60 kg, and that mass is 99.99% in the nucleons, then we can just take the number of humans in the world times their mass, divide by the nuclear mass density (which is the number density times the mass of a nucleon).
A nucleon (proton or neutron) is about 1.5 femtometers across, which is 1.5x10-15 meters. So the number density of nuclear matter is about 0.1 nucleons per cubic fermi, or 0.1 fm-3. I don't have a source for these and I don't care to google it; these are just the numbers I have at my finger tips for my research, but if you'd like to know more you can google the "nuclear saturation density."
Anyway, if the average person has a mass of about 60 kg, and that mass is 99.99% in the nucleons, then we can just take the number of humans in the world times their mass, divide by the nuclear mass density (which is the number density times the mass of a nucleon).
A nucleon (proton or neutron) is about 1.5 femtometers across, which is 1.5x10-15 meters. So the number density of nuclear matter is about 0.1 nucleons per cubic Fermi, or 0.1 fm-3. I don't have a source for these and I don't care to google it; these are just the numbers I have at my finger tips for my research, but if you'd like to know more you can google the "nuclear saturation density."
Anyway, if the average person has a mass of about 60 kg, and that mass is 99.99% in the nucleons, then we can just take the number of humans in the world times their mass, divide by the nuclear mass density (which is the number density times the mass of a nucleon).